01 - assembly alternatives
MitoFinder
By default, MitoPilot uses GetOrganelle to assemble the mitochondrial genome. GetOrganelle will only assemble the subset of reads which it identifies as mitochondrial. This makes it a very fast assembler that tends to work best if you have a sufficient reference database (more on that later). However, there may be cases where GetOrganelle produces unsatisfactory results.
If you wish to try a different assembly method, we have also implemented MitoFinder in MitoPilot. Unlike GetOrganelle, MitoFinder performs a complete assembly of all your reads using MEGAHIT, MetaSPAdes, or IDBA-UB. This makes it far slower, but can sometimes be more effective for organisms with few or poor reference mitogenomes.
MitoFinder can be selected as the assembler in the Assembly Opts. window of the Assemble module.
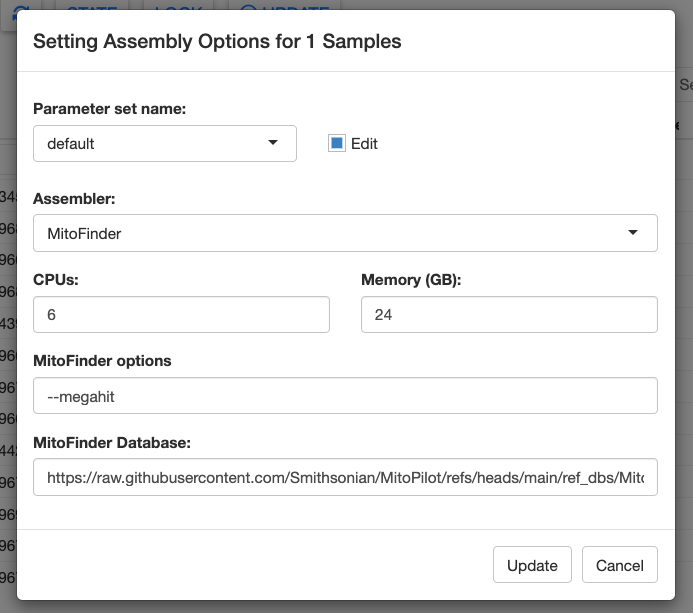
The defaults for MitoFinder are the MEGAHIT assembler and the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) reference mitochondrial genome. You can easily supply your own reference mitogenome(s) by specifying the full path to a GenBank formatted (.gb) file.
Importing External Assemblies
In some cases, GetOrganelle and MitoFinder can both fail to produce mitochondrial genome assemblies. You may wish to explore other assembly options outside of MitoPilot, such as the Geneious “map to reference” method.
If you still want to use MitoPilot for annotation and curation, you can import your own mitogenome assemblies. To do so, you will need to initialize a new MitoPilot project. A single project can only contain either assemblies generated by MitoPilot or assemblies generated by external software.
To set up a project with external assemblies, use the new_project_userAsmb function. This function requires the argument assembly_path, which is the full path to the directory containing all of your mitogenome assembly FASTA files. There should be one file (and one assembly) per sample.
The new_project_userAsmb function also requires two new columns in the mapping file:
Assembly: mitogenome assembly FASTA file names (one contig/scaffold sequence per sample)Topology: assembly topology, “circular” or “linear”
Once you have created a new project with this function, you can proceed to open the GUI and run MitoPilot. Note that you will still need to run the Assemble module, but it will only be used to map reads and calculate coverage.